Answers
1. The empirical formula of the weak acid is H₂PO₃
2. The molecular formula of the weak acid is H₄P₂O₆
Data obtained from the question Mass of compound = 0.8821 gH = 0.0220 gP = 0.3374 gO = 0.8821 - (0.0220 + 0.3374) = 0.5227 gEmpirical formula =? Empirical formula =? Molecular formula =?1. How to determine the empirical formulaThe empirical formula of the compound can be obtained as follow:
Divide by their molar mass
H = 0.0220 / 1 = 0.022
P = 0.3374 / 31 = 0.01
O = 0.5227 / 16 = 0.03
Divide by the smallest
H = 0.022 / 0.01 = 2
P = 0.01 / 0.01 = 1
O = 0.03 / 0.01 = 3
Thus, the empirical formula of the compound is H₂PO₃
2. How to determine the molecular formula Empirical formula = H₂PO₃Molar mass of compound = 162 g/molMolecular formula =?Molecular formula = empirical × n = mass number
[H₂PO₃]n = 162
[(1×2) + 31 + (16×3)]n = 162
81n = 162
n = 162 / 81
n = 2
Molecular formula = [H₂PO₃]n
Molecular formula = [H₂PO₃]₂
Molecular formula = H₄P₂O₆
Learn more about empirical and molecular formula:
https://brainly.com/question/18680555
#SPJ1
Related Questions
Sort the five steps of the scientific method.
State problem
Conduct experiment
Interpret data
Draw conclusion
Form hypothesis
Answers
The correct order of the five steps of the scientific method is as follows:
State problem
Form hypothesis
Conduct experiment
Interpret data
Draw conclusion.
The scientific method is a systematic approach used by scientists to investigate and understand the natural world. The five steps of the scientific method, in their logical order, are as follows:
State problem: In this step, the scientist identifies and defines a specific question or problem to be investigated. The problem should be clear and well-defined to guide the rest of the scientific process.
Form hypothesis: A hypothesis is a proposed explanation or prediction for the problem stated in step one. It is an educated guess that can be tested through experiments and observations. The hypothesis should be based on prior knowledge and observations.
Conduct experiment: In this step, the scientist designs and performs experiments to test the hypothesis. The experiment is carefully planned and executed, and data is collected through observations and measurements.
Interpret data: Once the experiment is completed, the scientist analyzes the collected data. This involves organizing, graphing, and statistically analyzing the data to identify patterns and trends.
Draw conclusion: Based on the interpretation of the data, the scientist draws conclusions about whether the hypothesis is supported or not. The conclusions should be objective and supported by evidence obtained from the experiment.
It's important to note that while these steps are presented in a linear order, the scientific process is often iterative, with scientists revisiting and refining hypotheses, conducting further experiments, and building upon existing knowledge.
For more questions on Conduct experiment
https://brainly.com/question/30994979
#SPJ8
Write the electron configuration for each of the following ions: (a) As3– (b) I– (c) Be2+ (d) Cd2+ (e) O2– (f) Ga3+ (g) Li+ (h) N3– (i) Sn2+ (j) Co2+ (k) Fe2+ (l) As3+
Answers
Answer:
a) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶
b) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶
c) 1s²
d) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 4d¹⁰
e) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶
f) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰
g) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰
h) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶
j) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 4d¹⁰
k) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁶
l) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰
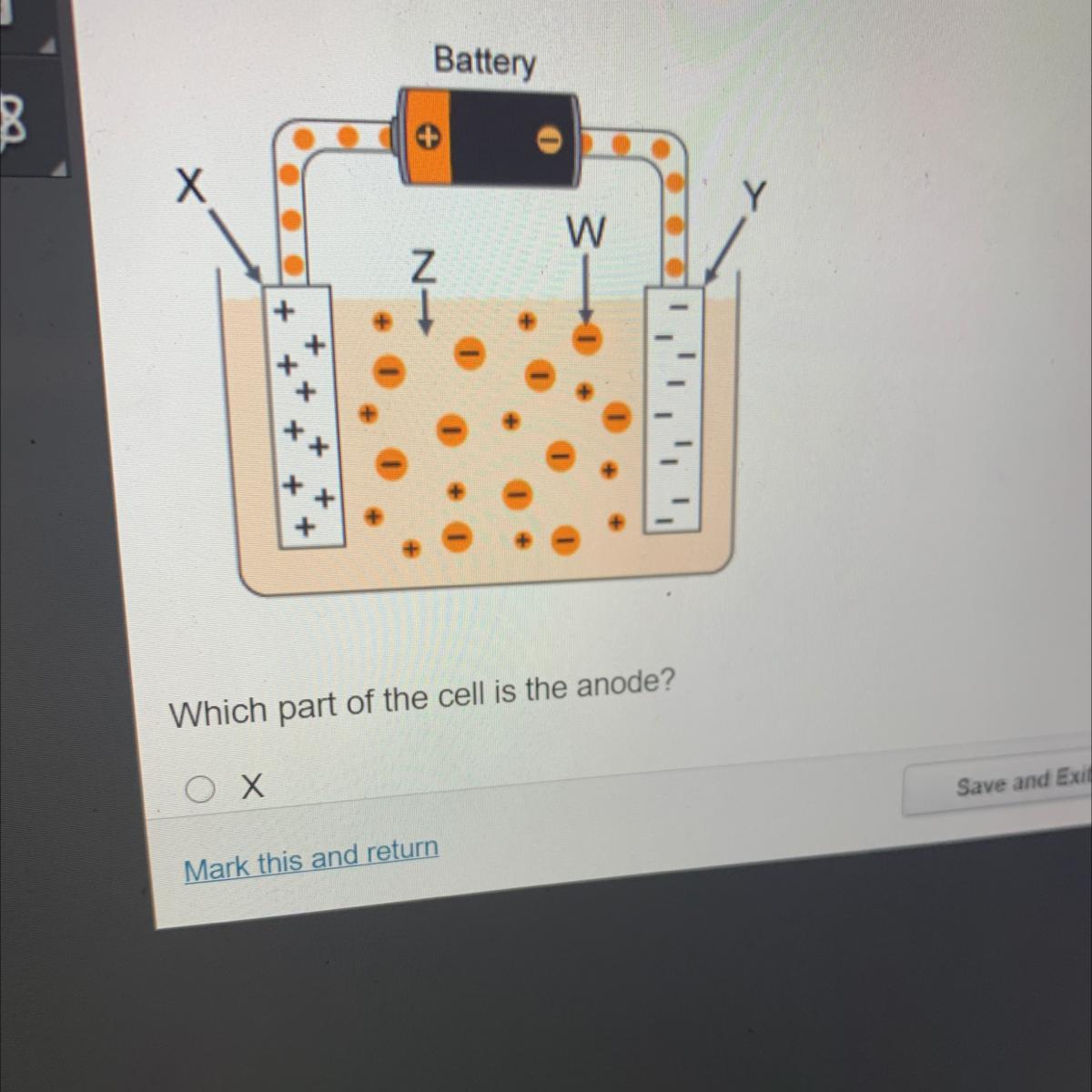
Which part of the cell is the anode?
Х
Y
W
Z
Answers
Stephan’s mother cuts a twig from a rose bush and plants it in the soil. After a few days, Stephan observes a new plant growing. Which characteristic does the growth of the new plant depict?
Answers
The growth of the new plant depicts the asexual reproduction characteristic. The characteristic that describes the growth of the new plant in Stephan's mother cutting a twig from a rose bush and planting it in the soil is asexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction is the mode of reproduction by which organisms generate offspring that are identical to the parent's without the fusion of gametes. Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which the offspring is produced from a single parent.
The offspring created are clones of the parent plant, meaning they are identical to the parent.The new plant in Stephan’s mother cutting a twig from a rose bush and planting it in the soil depicts the process of asexual reproduction, which is the ability of a plant to reproduce without seeds. In asexual reproduction, plants can reproduce vegetatively by cloning themselves using their roots, bulbs, or stems.
Know more about characteristic here:
https://brainly.com/question/28790299
#SPJ8
2 examples of metal’s catalytic reaction
Answers
Answer:
Example 1
palladium(II) nitrate,
Example 2
Metal catalysts such as Fe, Ni, Mo, and Co are routinely used in the manufacture of CNMs.
Explanation
The three metals used in catalytic converters — rhodium, platinum and palladium — are part of a category known as platinum group metals, or PGMs, which are known for their catalytic properties.
Why doesn't all soil look and feel the same? List 3 reasons
Answers
Answer:
all soil are also different due to how they were form
Calculate the activation energy in kJ/mol using data you calculated for rate constant at room temperature and cold temperature. ( R=8.314 J mol-1 K-1) Use the rearranged Arrhenius equation provided in the introduction for this calculation. Use T1 as your cold temperature and T2 as your room temperature, and k1 and k2 respectively. NOTE: Refer equation (4)
1. Rate Constant at room temperature:
2. Rate Constant at cold temperature
3. Temperature of the reaction mixture at room temperature
4. Temperature of the reaction mixture at cold temperature
5. Activation energy
Answers
The activation energy (Ea) in kJ/mol is equal to the product of the rearranged Arrhenius equation multiplied by 1000 kJ/mol.
To calculate the activation energy (Ea) in kJ/mol, you can use the rearranged Arrhenius equation (Equation 4):
Ea = R * (1/T2 - 1/T1) * ln(k2/k1)
Given:
k1 = Rate Constant at cold temperature
k2 = Rate Constant at room temperature
T1 = Temperature of the reaction mixture at cold temperature
T2 = Temperature of the reaction mixture at room temperature
R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1
Calculation:
Ea = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 * (1/T2 - 1/T1) * ln(k2/k1)
Ea = (8.314 J mol-1 K-1 * (1/T2 - 1/T1)) * ln(k2/k1)
Ea = (8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T2 - 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T1) * ln(k2/k1)
Ea = (8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T2 - 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T1) * ln(k2/k1)
Ea = (8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T2 - 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T1) * ln(k2/k1) * 1000 kJ/mol
Ea = (8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T2 - 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 / T1) * ln(k2/k1) * 1000 kJ/mol
Here you can learn more about Arrhenius equation
https://brainly.com/question/12907018#
#SPJ11
what is the water cycle
Answers
the water cycle is like a life cycle for water. it involves collected water, such as in an ocean, evaporating. also, water evaporates out of plants into the air through stomata. this is called transpiration. the water in the air is gas, now called water vapour. because the sky gets colder as you go up, the water vapour cools to the dew point and condenses, returning to a liquid state. The condensed water forms fall. This is called precipitation. When the precipitation hits the ground, it can do one of two things. It can infiltrate, or be absorbed into the ground. Or it can become runoff, which is the moving water after a rainfall. Then the runoff can join a river to be a part of a collected body of water, which starts the water cycle over again.
thanks, hope this opened up some insight.
Hydrogen reacts with oxygen according to the balanced equation
2H₂ (g) + O2(g) → 2H₂O(g). If X is the number of molecules of H₂ which react,
then the number of O2 molecules reacting is
Answers
Answer:
x/2
Explanation:
X = 2 molecules of H2
For 2 molecules of H2, there's only 1 molecule of O2. Meaning, there's twice the amount of H2, so O2 = x/2 molecules.
I hope I'm understanding this question right.
Lipids include:
A. fats and water
B. Oils and carbohydrates
C. Waxes and sterols
Answers
Answer: C
waxes and sterols
Explanation:
edge 2021
PROBLEM 19.12 Draw the structure of a triacylglycerol that fits each description: a. a saturated triacylglycerol formed from three 12-carbon fatty acids b. an unsaturated triacylglycerol that contains three cis double bonds c. a trans triacylglycerol that contains a trans double bond in each hydrocarbon chain
Answers
b. An unsaturated triacylglycerol that contains three cis double bonds would have three different unsaturated fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone. Each fatty acid would contain a cis double bond.
c. A trans triacylglycerol that contains a trans double bond in each hydrocarbon chain would have three different trans fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone. Each fatty acid would contain a trans double bond.
The gas in a balloon has a volume of 7.5 L at 100, kPa. The balloon is released into
the atmosphere, and the gas in it expands to a volume of 11 L. Assuming a constant
temperature, what is the pressure on the balloon at the new volume? What law did
you use to solve?
Answers
Answer:
please rate my answer 5 Star
Explanation:
Using Boyle's Law,
The pressure exerted by a gas is inversely proportional to the volume the gas is occupying provided the temperature is constant
p*v = constant
100*1000*7.5 = p * 11
p = 750000/11
Which two phrases describe the movement of thermal energy due to
convection currents in the water on Earth?
O A. From the bottom of the ocean to the surface
B. From the surface of the ocean to the bottom
C. From cooler parts of Earth to the equator
D. From the equator to cooler parts of Earth
Answers
Answer:
D. From the equator to cooler parts of Earth
Explanation:
Thermal energy is always transferred from an area with a higher temperature to an area with a lower temperature. Moving particles transfer thermal energy through a fluid by forming convection currents.
Answer:
B. From the surface of the ocean to the bottom
D. From the equator to cooler parts of Earth
Explanation:
Test approved
पर भारत में श्रीग्रामीण परिवारों की साख ने चार प्रमुख स्त्रोतों का वर्णन कीजि
ए।
Answers
Answer:
????????? i don't speak that language. sorry.
Explanation:
Use the standard reduction potentials located in the 'Tables' linked above to calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction:
2H+(aq) + Cu(s) H2(g) + Cu2+(aq)
Hint: Carry at least 5 significant figures during intermediate calculations to avoid round off error when taking the antilogarithm. You may use the OWL references to find the values you may need in this question.
Answers
Answer:
3.3 * 10^-12
Explanation:
The balanced equation of the reaction is;
2H+(aq) + Cu(s) ---------> H2(g) + Cu2+(aq)
Hence two electrons were transferred so n=2
E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
E°cell = 0 V - 0.34 V
E°cell = - 0.34 V
Then;
E°cell = 0.0592/n log K
Substituting values;
- 0.34 = 0.0592/2 log K
- 0.34/0.0296 = log K
-11.486 = log K
K = Antilog (-11.486)
K = 3.3 * 10^-12
Question 2 of 10
What is the percent yield of a reaction?
The amount of product obtained x 100
amount possible
B. The amount of product actually obtained in a reaction
C. The amount of product that is possible from a reaction
D. The difference between measured and calculated amounts
A.
Answers
Answer:
c
Explanation:
Use the data from the following figures to answer the questions below.
SUBSTANCE
DENSITY_9
cm
cork
0.22
water
1.0
sugar
1.6
aluminum
2.7
79
gold
19.3
02000 Ossewwe, in
The cube has a mass of 72.9 g.
iron
3 cm
3 cm
3 cm
2008 Ogsewu, in
What is its density in g/cm?
What substance is it?

Answers
Answer:
2.7g/cm³
Aluminum
Explanation:
Given parameters:
Mass of the cube = 72.9g
Unknown:
Density of the cube = ?
Solution:
To solve this problem, we need to find the density of the cube. The mass is given and the dimensions of the solid figure.
Now;
Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance
Density = \(\frac{mass}{volume}\)
Volume of the cube = L³ = 3³ = 27cm³
So;
Density = \(\frac{72.9}{27}\) = 2.7g/cm³
The body is aluminum because it has a density of 2.7g/cm³
Observe: Turn on Show molecular view, and notice the water molecules. Set the Water volume to 100 mL and the Powder mass to 20 g, and then click Play. Click Pause () after adding the powder. You should now see show some sodium acetate in the water.
What color represents the bonds between the particles of NaC2H3O2?
Click Play. Watch the animation a few times. What happens to the NaC2H3O2 bonds?
What happens to the bonds between water molecules?
Answers
Answer: how old are you
Explanation:
When recommending solutions to decrease human impact, which location were you able to make the greatest positive impact? Please explain your selection by using data from the simulation.
What recommendations would you give to your local community to help to decrease the local effects of human impact on the environment? List 2 recommendations and how they will positively impact your community.
What recommendations would you give to the global governments to help decrease the global effects of human impact on the environment? List 2 recommendations and how they will positively impact our planet.
Answers
When recommending solutions to decrease human impact, which location were you able to make the greatest positive impact? Please explain your selection by using data from the simulation.
New york, 893 - 853 = 40 which is the highest quotient.
What recommendations would you give to your local community to help to decrease the local effects of human impact on the environment? List 2 recommendations and how they will positively impact your community.
Installing solar panels and replanting 2 trees for every tree that’s been cut down, this will help the atmosphere and deforestation.
What recommendations would you give to the global governments to help decrease the global effects of human impact on the environment? List 2 recommendations and how they will positively impact our planet.
Constructing using only recycled materials decreases water pollution to 823 ppm and Creating more protected areas decreases air pollution to 368 ppm this will help the environment and oxygen.
Answer:
........
Explanation:

A 500 mL gas sample is collected over water at a pressure of 740mmHg and 25°C. What is the volume of the dry gas at STP? (STP = 1 atm and 0°C) Vapor pressure at 25° of H2O equals 24mmHg.
Answers
1) List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: gas.
Volume: 500 mL.
Pressure: 740 mmHg
Temperature: 25 ºC.
Vapor pressure at 25 ºC: 24 mmHg.
2) Pressure of the gas.
\(P_{gas}=P_{atm}-P_{water\text{ }vapor}\)\(P_{gas}=740\text{ }mmHg-24\text{ }mmHg\)\(P_{gas}=716\text{ }mmHg\)The pressure of the gas is 716 mmHg
3) Moles of gas
3.1- List the known quantities.
Volume: 500 mL.
Temperature: 25 ºC.
Pressure: 716 mmHg.
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1).
3.2- Set the equation.
\(PV=nRT\)3.3- Convert the units of the volume, the temperature, and the pressure.
Volume.
1 L = 1000 mL
\(L=500\text{ }mL*\frac{1\text{ }L}{1000\text{ }mL}=0.500\text{ }L\)Temperature.
\(K=25\text{ }ºC+273.15\text{ }K\)\(K=298.15\text{ }K\)Pressure
1 atm = 760 mmHg
\(atm=716\text{ }mmHg*\frac{1\text{ }atm}{760\text{ }mmHg}=0.942\text{ }atm\)3.4- Plug in the know quantities in the ideal gas equation.
\((0.942\text{ }atm)(0.500\text{ }L)=n*(0.082057\text{ }L*atm*K^{-1}*mol^{-1})(298.15\text{ }K)\)3.5- Solve for n (moles).
Divide both sides by (0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1)) * (298.15 K)
\(\frac{(0.942atm)(0.500L)}{(0.082057\text{ }L*atm*K^{-1}mol^{-1})(298.15K)}=\frac{n(0.082057\text{ }L*atm*K^{-1}mol^{-1})(298.15K)}{(0.082057\text{ }L*atm*K^{-1}mol^{-1})(298.15K)}\)\(n=\frac{(0.942atm)(0.500L)}{(0.082057L*atm*K^{-1}*mol^{-1})(298.15K)}=\)\(n=0.0193\text{ }mol\)
4) Dry volume at STP
STP conditions are
Temperature: 273 K
Pressure: 1 atm.
At STP conditions 1 mol of a gas occuppies 22.4 L. We can use this as a conversion factor.
1 mol gas = 22.4 L
\(V=0.0193\text{ }mol\text{ }gas*\frac{22.4\text{ }L}{1\text{ }mol\text{ }gas}=0.432\text{ }L\)The volume of the dry gas at STP is 0.432 L.
.
Answer:
1) List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: gas.
Volume: 500 mL.
Pressure: 740 mmHg
Temperature: 25 ºC.
Vapor pressure at 25 ºC: 24 mmHg.
2) Pressure of the gas.
The pressure of the gas is 716 mmHg
3) Moles of gas
3.1- List the known quantities.
Volume: 500 mL.
Temperature: 25 ºC.
Pressure: 716 mmHg.
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1).
3.2- Set the equation.
3.3- Convert the units of the volume, the temperature, and the pressure.
Volume.
1 L = 1000 mL
Temperature.
Pressure
1 atm = 760 mmHg
3.4- Plug in the know quantities in the ideal gas equation.
3.5- Solve for n (moles).
Divide both sides by (0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1)) * (298.15 K)
4) Dry volume at STP
STP conditions are
Temperature: 273 K
Pressure: 1 atm.
At STP conditions 1 mol of a gas occuppies 22.4 L. We can use this as a conversion factor.
1 mol gas = 22.4 L
The volume of the dry gas at STP is 0.432 L.
Explanation:
what does the first ionization energy represent?
A. the energy required to add an electron
B. the energy to remove an energy level of electrons
C. the energy required to remove an electron from an atom
D. the energy given off when an electron is gained
Answers
The first ionization energy represents Option C. the energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
The ionization energy is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion to form a cation that carries a charge of +1.Ionization energy is an essential property of an element, and it is determined by the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) and the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus. The effective nuclear charge is the positive charge that an electron experiences from the nucleus.
The closer the valence electrons are to the nucleus, the greater the effective nuclear charge, making it more challenging to remove an electron from the atom. The ionization energy increases from left to right and from bottom to top across the periodic table. The ionization energy decreases from top to bottom and from right to left across the periodic table. The reason for this trend is the increase in atomic radius and the decrease in effective nuclear charge from top to bottom and from right to left on the periodic table.
Ionization energy plays a significant role in chemical reactions, particularly in redox reactions. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion is equivalent to the energy released when the ion or atom gains an electron. A high ionization energy indicates that the atom is less reactive and more stable since it requires a lot of energy to remove an electron. Therefore the correct option is C
Know more about ionization energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/20658080
#SPJ8
The decomposition of cyclohexane to benzene and Martialism is a high mass transfer limited period on the planet. The reaction will be carried out in a tubular reactor with an internal diameter of 5 cm and a length of 20 m; the pipes are filled with cylindrical pellets 0.5 cm in diameter and 0.5 cm in length. The pellets are only covered with the outer surface coating. The filled bed porosity is 40%. The inlet flow rate is 60 dm3/min.
Plot the tubular length vs. conversion graph when the inlet gas stream contains 5% cyclohexane and 95% hydrogen at 2 atm and 500°C. What would be the required tubular length for 99.9% conversion?
For cyclohexane diffusion in hydrogen, use the Fuller, Schettler, and Giddings Correlation given below.

Answers
The required tubular length for 99.9% conversion is 116.84 meters.
On Earth, the rate at which cyclohexane reacts with benzene and methylcyclopentane is constrained by high mass transfer.
A tubular reactor with an internal diameter of 5 cm and a length of 20 m will be used to conduct the reaction, and cylindrical pellets with dimensions of 0.5 cm in diameter and 0.5 cm in length will be placed within the reactor's pipes.
Only the exterior surface of the pellets are coated.
The packed bed has a 40% porosity and a 60 dm3/min intake flow rate.
When the intake gas stream includes 5% cyclohexane and 95% hydrogen at 2 atm and 500°C, the tubular length vs. conversion graph should be drawn.
The graph may be used to identify the minimum length of tube necessary for 99.9% conversion.
For cyclohexane diffusion in hydrogen, the Fuller, Schettler, and Giddings Correlation is as follows:
a = 0.8854,
b = 1.764102,
C = 6.0231023.
The tube length vs. conversion graph may be displayed at 2 atm and 500°C when the incoming gas stream includes 5% cyclohexane and 95% hydrogen.
The following equation may be used to determine the rate of reaction:
ra=2.31011 exp[-88580/RT]C_A(1X)/3
The mole balancing equation for an isothermal tubular reactor is given as
dX/dL = -ra/C A,
where X is the conversion and L is the length.
To determine the length of the tubular reactor needed for a specific conversion X, we can integrate the aforementioned equation from X = 0 to X = X.
We must numerically calculate the following equation to obtain the necessary tube length for 99.9% conversion:
∫0.999L0−ra/CA
dL=0.999XEq L
for X=0.999
After rearranging the equation above, we get:
0.999L0ra/CA
dL=XX Eq
The aforementioned equation is integrated to give us
L = 116.84 m.
Therefore, the required tubular length for 99.9% conversion is 116.84 meters.
For such more questions on length
https://brainly.com/question/13253944
#SPJ8
What is the form of water in the earth’s surface
Answers
Which of the following is common to all fields of engineering?
A. Predicting how technology will interact with human tissue
B. The importance of biocompatible materials
c. Use of the engineering process
D. Use of devices that don't require an external power source
Answers
Answer:
C Use of engineering process
Guysss how to explain nuclear chemistry? And define nuclear chemistry ?
Answers
Answer:
How do amoeba respire.
Define Diffusion.
A man hits a golf ball (0.2kg) which accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s². What amount of
tric force acted on the ball? Complete the table below to show all of your work.
then there’s a triangle with f at the top m in the left and a in the right
Answers
Answer:
F = ma, where F is the force acting on the body, m is the mass of the body, and a is the acceleration of the body. Therefore, the force acting on the ball is 4Newtons.
Explanation:
HBrO3
A. All non metals “acid subcategory”
Answers
what mass of glucose c6h12o6 would be required to prepare 5000 mL of a 0.215 M solution
Answers
Approximately 194.0 grams of glucose (C6H12O6) would be required to prepare a 5000 mL solution with a concentration of 0.215 M.
To determine the mass of glucose (C6H12O6) required to prepare a 0.215 M solution in 5000 mL, we need to use the formula:
Molarity (M) = moles of solute / volume of solution (in liters)
First, let's convert the volume of the solution from milliliters (mL) to liters (L):
5000 mL = 5000/1000 = 5 L
Now, we can rearrange the formula to solve for moles of solute:
moles of solute = Molarity (M) x volume of solution (L)
moles of solute = 0.215 M x 5 Lmoles of solute = 1.075 mol
Since glucose (C6H12O6) has a molar mass of approximately 180.16 g/mol, we can calculate the mass of glucose using the equation:
mass of solute = moles of solute x molar mass of solute
mass of glucose = 1.075 mol x 180.16 g/mol
mass of glucose = 194.0 g (rounded to three significant figures)
Therefore, approximately 194.0 grams of glucose (C6H12O6) would be required to prepare a 5000 mL solution with a concentration of 0.215 M. It's important to note that the molar mass of glucose used in this calculation may vary slightly depending on the level of precision required.
For more such questions on glucose visit:
https://brainly.com/question/397060
#SPJ8
7 of 207 of 20 Items
10:54
Question
Most foxes are brown or orange in color. However, foxes are light silver or nearly white in the far northern tundra. What is a MOST LIKELY reason for this color difference?
Responses
A Arctic foxes have developed teeth that allow them to eat frozen carrion.Arctic foxes have developed teeth that allow them to eat frozen carrion.
B Arctic foxes have developed coloring based on their nonliving environment.Arctic foxes have developed coloring based on their nonliving environment.
C Arctic foxes have developed hunting habits that helps them find food.Arctic foxes have developed hunting habits that helps them find food.
D Arctic foxes have developed special eye coverings that let them see even during blizzards.
Answers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Most animals change due to the environment to help them live better
Calculate [H3O+] and [OH−] for each of the following solutions at 25 ∘C given the pH.
pH= 11.22
Answers
Answer: The value of \([H_{3}O^{+}]\) is \(6.025 \times 10^{-12}\) M and \([OH^{-}]\) is \(1 \times 10^{-14}\).
Explanation:
pH is the negative logarithm of concentration of hydrogen ion.
It is given that pH is 11.22. So, the value of concentration of hydrogen ions is calculated as follows.
\(pH = - log [H^{+}]\\11.22 = - log [H^{+}]\\conc. H^{+} = 6.025 \times 10^{-12}\) M
Let the value \(6.025 \times 10^{-12}\) is considered as equal to 0. Hence, the relation between pH and pOH value is as follows.
pH + pOH = 14
0 + pOH = 14
pOH = 14
Now, pOH is the negative logarithm of concentration of hydroxide ions.
Hence, \([OH^{-}]\) is calculated as follows.
\(pOH = - log [OH^{-}]\\14 = - log [OH^{-}]\\conc. OH^{-} = 1 \times 10^{-14} M\)
Thus, we can conclude that the value of \([H_{3}O^{+}]\) is \(6.025 \times 10^{-12}\) M and \([OH^{-}]\) is \(1 \times 10^{-14}\).