Answers
Answer:
\(m=0.512m\)
Explanation:
Hello,
In this case, we can consider the n-propanol as the solute (lower amount) and the t-butanol as the solvent (higher amount), for which, initially, we must compute the moles of n-propanol (molar mass = 60.1 g/mol) as shown below:
\(n_{solute}=0.400g*\frac{1mol}{60.1g0}=6.656x10^{-3}mol\)
Since the molality is computed via:
\(m=\frac{n_{solute}}{m_{solvent}}\)
Whereas the mass of the solvent is used in kilograms (0.0130g for the given one). Thus, we compute the resulting molality of the solution:
\(m=\frac{6.656x10^{-3}mol}{0.0130kg}\\ \\m=0.512\frac{mol}{kg}\)
Or just:
\(m=0.512m\)
Best regards.
Related Questions
What might have been the advantages and disadvantages of just having
experienced polar explorers at the catlin arctic survey.
Answers
While having experienced polar explorers at the Catlin Arctic Survey would have been beneficial in many ways, it would also have been important for them to work collaboratively with the rest of the team.
Advantages:
Experienced polar explorers would have had a wealth of knowledge and skills, such as how to travel over the ice, how to set up camp, and how to handle emergencies.
Experienced polar explorers would have been able to make informed decisions about the best routes to take and the most efficient ways to travel. This could have helped to save time and energy.
Disadvantages:
Experienced polar explorers may have been set in their ways and resistant to new ideas. This could have hindered the team's ability to adapt to changing circumstances and make the most of new opportunities.
Experienced polar explorers may have been overconfident and taken risks that the rest of the team was not comfortable with. This could have put everyone's safety at risk.
To learn more about the Catlin Arctic Survey, follow the link:
https://brainly.com/question/28313250
#SPJ1
2. In order to prepare a 0.523 m aqueous solution of potassium iodide, how many grams of potassium iodide must be added to 2.00 kg of water?
Answers
Therefore, we need to add 173.49 grams of potassium iodide to 2.00 kg of water to prepare a 0.523 m aqueous solution.
How is 1% potassium iodide solution made?Potassium iodide solution is made by dissolving 1 litre of water in 1 gramme of potassium iodide and 1 gramme of hydroxyammonium chloride. Solution of potassium iodide, about 0.2 M: 33 grammes of potassium iodide should be dissolved in 1 litre of water.
We must apply the following formula to get the mass of potassium iodide required to create a 0.523 m aqueous solution:
molarity=moles of solute/liters of solution
First, we must determine the solution's litre volume:
1 kg of water=1000 mL of water
2.00 kg of water = 2000 mL of water
Volume of solution = 2000 mL = 2.00 L
Next, we need to rearrange the formula to solve for the moles of solute:
moles of solute=molarity x liters of solution
moles of solute = 0.523 mol/L x 2.00 L = 1.046 mol
Finally, we can use the molar mass of potassium iodide (166.0028 g/mol) to convert the moles of solute to grams:
mass of potassium iodide = moles of solute x molar mass
mass of potassium iodide = 1.046 mol x 166.0028 g/mol = 173.49 g
To know more about potassium iodide visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/28099104
#SPJ1
what have you observed when you fill in a basin with water? how do you do it?
Answers
Answer:
Cautiously and avoiding filling in the central area so that it does not overflow when filling, since being very beach makes filling difficult.
Explanation:
The basins are shallow, that is why filling is difficult, the filling must be slow, low intensity and at the edges not placing the water filling in the center of the basin.
When you fill a basin with liquid water, you can see that the water takes the shape of the container in which it is contained. This is because in the liquid state, water has molecules farther apart than in the solid state.
You can notice this property when performing an experiment with liquid and solid water.
When filling a glass, liquid water takes on the shape of a glass, and solid water, such as an ice cube, remains the same shape when placed in a glass.
Therefore, when filling a basin with water we perceive a property of the physical state of water, in liquid form. Water is one of the few substances that can be found naturally in liquid, solid and gaseous states.
Learn more here:
https://brainly.com/question/23650420
One of the hydrates of CoCl2 is cobalt(II) chloride dihydrate . A 56.2 gram sample of CoCl2 2 H2O was heated thoroughly in a porcelain crucible, until its weight remained constant. After heating, how many grams of the anhydrous compound remained?
Answers
The formula for cobalt(II) chloride dihydrate is CoCl2 · 2H2O, which means that each mole of this compound contains 1 mole of CoCl2 and 2 moles of H2O. To find the number of moles of CoCl2 in 56.2 grams of CoCl2 · 2H2O, we need to first find the molar mass of the compound:
Molar mass of CoCl2: 58.933 g/mol
Molar mass of 2H2O: 36.032 g/mol (2 × 18.016 g/mol)
Molar mass of CoCl2 · 2H2O: 58.933 g/mol + 36.032 g/mol = 94.965 g/mol
Now we can find the number of moles of CoCl2 in 56.2 grams of CoCl2 · 2H2O:
56.2 g / 94.965 g/mol = 0.591 moles
Since each mole of CoCl2 · 2H2O contains 1 mole of CoCl2, there are also 0.591 moles of CoCl2 in the sample.
We are told that the hydrate was heated until its weight remained constant, which means that all of the water was driven off and only the anhydrous CoCl2 remained. If the percent yield of the reaction was 100%, we would expect to recover the same amount of CoCl2 that was in the original sample (0.591 moles). However, we are told that the percent yield was only 65.5%, which means that the actual amount of CoCl2 recovered was:
0.655 × 0.591 moles = 0.387 moles
To find the mass of the anhydrous CoCl2 that remained, we can use the molar mass of CoCl2:
Molar mass of CoCl2: 58.933 g/mol
0.387 moles × 58.933 g/mol = 22.8 grams
Therefore, after heating, 22.8 grams of anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride remained.
How is the rate of a chymotrypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by using more enzyme in the reaction mixture
Answers
The rate of a chymotrypsin-catalyzed reaction will increase by using more
enzyme in the reaction mixture.
The rate of a chemical reaction and the enzyme concentration have a direct
relationship. As concentration increases, the rate of a chemical reaction
also increases and vice versa.
In this scenario, we were told more enzyme was used in the reaction mixture
which signifies an increase in the concentration and a corresponding
increase in the rate of reaction.
Read more on https://brainly.com/question/12330608
what will I benefit or what will I gain if I know the absorbance and emission of any substance?
Answers
How many sulfur atoms are in 5 SF6 ?
Answers
Answer:
The molecular formula for sulfur hexafluoride is SF6 S F 6 , in which there is 1 sulfur atom and 6 fluorine atoms.
Explanation:
hope this helps
NO LINKS/ please round two decimal places !!

Answers
if two substances have a the same mass but substance A has a higher density than substance B, which one will have the higher volume?
Answers
Answer: So I think A will have the higher volume
for the reaction at 400. k, . find the value of k for each of the following reactions at the same temperature:
Answers
The value of Kp for each of the reactions are 0.024 atm²; 6.4 atm⁻¹; and 1.681 x 10³ atm⁻⁴.
What is equilibrium constant?Equilibrium constant expression regarding the partial pressure is designated as Kp. Equilibrium constant Kp is same as the partial pressure of products divided by partial pressure of reactants and the partial pressure are increased with some power that is equal to the coefficient of the substance in balanced equation.
Pressure doesn’t affect the value of Kp, as concentration also doesn’t affect the value of Kc. A raise in pressure causes equilibrium to shift in favor of the direction with the fewer moles, so then the pressure reduces. The partial pressure ratio of reactant to products remains the same so Kp doesn’t change.
In this case, value of Kp for each of the following reactions are:
(i) 2NH₃ ⇌ N₂ +3H₂;
Kp = [H₂]³[N₂] / [NH₃]² = [ [NH₃]² / [N₂][H₂]³ ]⁻¹ = (41)⁻¹ = 1 / 41 = 0.024 atm²
(ii) 1/2N₂ + 3/2H₂ ⇌ NH₃;
Kp = [NH₃] / [H₂]³⁻² [N₂]¹⁻² = [ [NH₃]² / [H₂]³ [N₂] ]¹⁻² = (41)¹⁻² = 6.4 atm⁻¹
(iii) 2N₂ + 6H₂ ⇌ 4NH₃.
Kp = [NH₃]⁴ / [N₂]² [H₂]⁶ = [ [NH₃]² / [N₂][H₂]³ ]²= (41)² = 1.681 × 10³ atm⁻⁴
Learn more about equilibrium constant at: https://brainly.com/question/10038290
#SPJ4
Although part of your question is missing, you might be referring to this full question: For the reaction N₂ + 3H₂ ⇌ 2NH₃. At 400 K, Kp = 41 atm⁻². Find the value of Kp for each of the following reactions at the same temperature:
(i) 2NH₃ ⇌ N₂ +3H₂;
(ii) 1/2N₂ + 3/2H₂ ⇌ NH₃;
(iii) 2N₂ + 6H₂ ⇌ 4NH₃.
A 10.57 g sample of an unknown metal was heated to 100.00 ºC in boiling water and then transferred to a 104.0 g water bath at 22.50ºC. The temperature of the water bath rose to a maximum of 24.15ºC. What is the specific heat of the metal in cal/gºC ?
Answers
According to the problem the specific heat of the metal is 0.0329 cal/g°C.
What is specific heat?Specific heat is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree. It is usually expressed in units of joules per kilogram-kelvin (J/kg-K). It is an important physical property of a substance that affects the rate of heat transfer.
The specific heat of a metal can be calculated using the equation, q = mcΔT,
where q is the amount of heat energy,
m is the mass of the metal sample,
c is the specific heat, and
ΔT is the change in temperature. In this problem, q = 10.57 g × c × (24.15ºC - 22.50ºC) = 2.85 g × c.
The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of the water bath can be calculated using the equation q = mcΔT,
where q is the amount of heat energy, m is the mass of the water bath,
c is the specific heat of water (4.184 J/g°C), and
ΔT is the change in temperature. In this problem, q = 104.0 g × 4.184 J/g°C × (24.15ºC - 22.50ºC) = 86.67 J.
The specific heat of the metal can be calculated by dividing the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of the metal sample by the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of the water bath. This gives us c = 2.85 g × c / 86.67 J = 0.0329 cal/g°C.
Therefore, the specific heat of the metal is 0.0329 cal/g°C.
To learn more about specific heat
https://brainly.com/question/27862577
#SPJ1
Who determined the mass of the electron?
Answers
Answer:
This was determined with a precision of better than 1% by Robert A. Millikan in his famous oil drop experiment in 1909. Together with the mass-to-charge ratio, the electron mass was thereby determined with reasonable precision.
which is the graph of the function g(x) = f(-x)
Answers
To graph the function g(x) = f(-x), you can start with the graph of f(x) and then reflect it about the y-axis.
What is a graph of the function g(x) = f(-x)?To find the graph of the function g(x) = f(-x), we can start with the graph of the function f(x) and then reflect it about the y-axis.
If the graph of f(x) is symmetric with respect to the y-axis, meaning it is unchanged when reflected, then g(x) = f(-x) will have the same graph as f(x).
However, if the graph of f(x) is not symmetric with respect to the y-axis, then g(x) = f(-x) will be a reflection of f(x) about the y-axis.
In either case, the resulting graph of g(x) = f(-x) will be symmetric with respect to the y-axis.
Learn more about the graph of functions at: https://brainly.com/question/17089414
#SPJ1

Mg(s) + Ni2+(ag) -> Mg2+ (aq) + Ni(s) What is the total number of moles of electrons lost by Mg(s) when 2.0 moles of electrons are gained by Ni2+(ag)? * 10 ( 1.0 mol ,20 mol ,3.0 mol, 4.0 mol
Answers
The total number of moles of electrons lost by Mg(s) when 2.0 moles of electrons are gained by Ni2+(ag) is also 2.0 moles of electrons.
How to find the number of moles?This is because in a chemical equation, the number of moles of electrons gained by the reducing agent (in this case Ni2+) is equal to the number of moles of electrons lost by the oxidizing agent (in this case Mg(s)).
In this redox reaction, Mg is being oxidized because it loses electrons and Ni is being reduced because it gains electrons. The oxidation and reduction process are occurring simultaneously, so the number of electrons lost by Mg(s) is equal to the number of electrons gained by Ni2+(ag).
Learn more about moles of electrons in brainly.com/question/512038
#SPJ1
The electrons that are gained by the \(Ni^{2+}\) ion is 2.0 moles of electrons.
What is the number of the electrons gained?We know that when there is a redox reaction, there would be the loss or gain of electrons in the process. The process is a simultaneous one so the electrons that are lost by one specie must as a matter of necessity be gained by another specie.
In this case, as we look at the reaction equation we can see that there are two electrons that have been lost by the magnesium atom and these two electrons would be gained by the Nickel II ion.
Learn more about redox reaction:https://brainly.com/question/13293425
#SPJ1
how to convert anisole to salicylic acid
Answers
Answer:
ipfiyf8y97guog7
Explanation:
oyviyvhlvoyvhlvouuoupvpu
the density of an object does not change when you change the shape of it because
Answers
Answer: The density of an object can change
Density is an intensive property. This means that regardless of the object's shape, size, or quantity, the density of that substance will always be the same. Even if you cut the object into a million pieces, they would still each have the same density.
Density is an intensive property. This means that regardless of the object's shape, size, or quantity, the density of that substance will always be the same. Even if you cut the object into a million pieces, they would still each have the same density
You are a paleontology professor working at a dig site looking for fossils. You come across a deposit that is emitting radiation. Upon further testing you find that the sample is changing from carbon (atomic number 6) into nitrogen (atomic number 7) as radiation is emitted. What type of radiation is it?
Answers
Answer:
β particles
Explanation:
The most common radioactive isotope of carbon is C-13.
The unbalanced nuclear equation is
\(\rm _{6}^{13}C \longrightarrow \, ? + \, _{7}^{13N}\)
Let's write the question mark as a nuclear symbol.
\(\rm _{6}^{13}C} \longrightarrow \, _{Z}^{A}X+ \, _{7}^{13}N\)
The main point to remember in balancing nuclear equations is that the sums of the superscripts and the subscripts must be the same on each side of the equation.
Then
13 = A + 13, so A = 13 - 13 = 0, and
6 = Z + 7, so Z = 6 - 7 = -1
Then, your nuclear equation becomes
\(\rm _{6}^{13}C \longrightarrow \, _{-1}^{0}M + \, _{7}^{13}N\)
The particle with "zero" mass and a charge of -1 is an electron, so the balanced nuclear equation is
\(\rm _{6}^{13}C \longrightarrow \, _{-1}^{0}e + \, _{7}^{13}N\)
The radiation consists of β particles (electrons)
Answer:
I think think that the one above me is beta radiation
Explanation:
At what temperature
(Celsius) will water change from a
liquid to solid?
Answers
Answer:
0 degrees Celsius
Explanation:
Answer:
Water changes from a liquid to a solid at 0° Celsius
What is the pressure, in atmospheres, exerted by a 0.100 mol sample of oxygen in a 2.00 L container at 273 °C? A) 4.48 x 10¹¹ atm B) 2.24 x 10⁰ atm C) 1.12 x 10³ atm D) 2.24 x 10³ atm
Answers
The pressure, in atmospheres, exerted by a 0.100 mol sample of oxygen in a 2.00 L container at 273 °C is 2.24 × 10⁰ atm.
How to calculate pressure?The pressure of a substance can be calculated using the following formula;
PV = nRT
P = pressureV = volumen = no of molesR = gas law constantT = temperatureAccording to this question, the pressure, in atmospheres, exerted by a 0.100 mol sample of oxygen in a 2.00 L container at 273 °C can be calculated as follows:
P × 2 = 0.1 × 0.0821 × 546
2P = 4.48266
P = 2.24 × 10⁰ atm
Learn more about pressure at: https://brainly.com/question/31525061
#SPJ1
946.36 water * 1 mol water/ 236.59 g water * 4 mol lemonade/ 2 mol water * 225.285 g lemonade/1 mole lemonade = ? g lemonade.
Answers
According to the recipe, to make 4 moles of lemonade, you use 2 moles of water, one mole of sugar and one mole of lemon juice, expressed in grams:
2 water + sugar + lemon juice = 4 lemonade
2*(236.59) + 225g + 257.83g = 4*(719.42)g
473.18g + 225g + 257.83g = 2877.68g
So for every 2877.68g of lemonade made, they use 473.18g of water, 225g of sugar, and 257.83g of lemon juice.
You know that they made a batch of 2050.25g, so to detect the limiting reactant, first, you have to calculate, in theory, how much of each ingredient you need to make the given amount of lemonade:
Use cross multiplication
Water:
2877.68g lemonade → 473.18g water
2050.25g lemonade → X= (2050.25*473.18)/2877.68= 337.12g water
Following the recipe, to elaborate 2050.25g of lemonade, you need to use 337.12g of water.
Sugar:
2877.68g lemonade → 225g sugar
2050.25g lemonade → X= (2050.25*225)/2877.68= 160.30g sugar.
To elaborate 2050.25f of lemonade you need to use 160.30g of sugar.
Lemon juice:
2877.68g lemonade → 257.83g lemon juice
2050.25g lemonade → X= (2050.25*257.83)/2877.68= 183.69g lemon juice.
To elaborate 2050.25f of lemonade you need to use 183.69g lemon juice.
Available ingredients vs. theoretical yields for 2050.25g of lemonade:
Water 946.36 g → 337.12g
Sugar 196.86 g → 160.30g
Lemon Juice 193.37 g → 183.69g
The lemon juice will be the first ingredient to be used up, there will be a surplus of water and sugar.
What is lemonade?
In Egypt around the 13th and 14th centuries, people drank a concoction of lemon juice, dates, and honey called qatarmizat.Lemonade was sold to Parisians in cups by vendors who carried tanks of the soft drink on their backs.To know more about lemonade, click the link given below:
https://brainly.com/question/12484449
#SPJ1
Determine the volume (in mL) of 1.00 M NaOH that must be added to 250 mL of 0.50 M CH3CO₂H to produce a buffer with a pH of 4.50.
Answers
Approximately 70.57 mL of 1.00 M NaOH should be added to 250 mL of 0.50 M CH3CO₂H to produce a buffer with a pH of 4.50.
To determine the volume of 1.00 M NaOH required to produce a buffer with a pH of 4.50 when added to 250 mL of 0.50 M CH3CO₂H, we need to consider the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation and the stoichiometry of the reaction.
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for a buffer solution is given as:
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA])
In this case, CH3CO₂H (acetic acid) acts as the weak acid (HA) and CH3COO- (acetate ion) acts as its conjugate base (A-). We are given that the desired pH is 4.50, and we can determine the pKa value for acetic acid from reference sources, which is approximately 4.75.
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, we can rearrange it to solve for the ratio [A-]/[HA]:
[A-]/[HA] = 10^(pH - pKa)
[A-]/[HA] = 10^(4.50 - 4.75) = 10^(-0.25) = 0.5623
This means that the ratio of the acetate ion to acetic acid in the buffer solution should be approximately 0.5623.
To calculate the required volume of NaOH, we need to consider the stoichiometry of the reaction. Acetic acid reacts with hydroxide ions (OH-) to form acetate ions and water:
CH3CO₂H + OH- → CH3COO- + H2O
The stoichiometric ratio between acetic acid and hydroxide ions is 1:1. Therefore, the volume of 1.00 M NaOH needed can be calculated using the equation:
Volume (NaOH) × 1.00 M = Volume (CH3CO₂H) × 0.50 M × 0.5623
Volume (NaOH) = (Volume (CH3CO₂H) × 0.50 M × 0.5623) / 1.00 M
Volume (NaOH) = (250 mL × 0.50 M × 0.5623) / 1.00 M
Volume (NaOH) ≈ 70.57 mL
For more such questions on buffer visit:
https://brainly.com/question/13076037
#SPJ8
moles of each product that would form as a result of the decomposition of aspirin
Answers
The decomposition of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid,\(C_{9} H_{8} O_{4}\)) can occur through the hydrolysis reaction, resulting in the formation of acetic acid (\(CH_{3} COOH\)) and salicylic acid (\(C_{7} H_{6}O_{3}\)).
The decomposition of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, \(C_{9} H_{8} O_{4}\)) can occur through the hydrolysis reaction, resulting in the formation of acetic acid (\(CH_{3} COOH\)) and salicylic acid (\(C_{7} H_{6}O_{3}\)). To determine the moles of each product formed, we need to consider the balanced chemical equation for the reaction:
\(C_{9} H_{8} O_{4} = > C_{7} H_{6}O_{3} +CH_{3} COOH\)
From the equation, we can see that for every 1 mole of aspirin, 1 mole of salicylic acid and 1 mole of acetic acid are produced.
Therefore, the moles of salicylic acid and acetic acid formed will be equal to the number of moles of aspirin that decomposes. If we know the amount of aspirin in moles, we can directly calculate the moles of each product based on stoichiometry.
For more question on aspirin
https://brainly.com/question/25794846
#SPJ8
how to solve x² in differential
Answers
Answer:
x² = mutiphy by them self
Explanation:
what the the noble gas configuration for krypton
Answers
Answer:
[Ar] 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p⁶
Explanation:
Krypton is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often used with other rare gases in fluorescent lamps. With rare exceptions, krypton is chemically iner,
Arrange the objects from smallest to largest.
Answers
According to the problem Arrange the objects from smallest to largest is Pencil, Pillow, Basketball, House.
What is smallest?The smallest unit of measurement is the atom, which is the smallest particle of an element that still retains its chemical identity. Atoms are composed of even smaller particles, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. The size of an atom can vary depending on the element, but they typically measure between 0.1 and 0.5 nanometers in diameter.The smallest unit of measurement is the Planck Length, which is 1.616229 x 10-35 meters. This is the smallest measurement of length that is possible in the universe. It is also the smallest unit of measurement that has a meaning in physics.
To learn more about smallest
https://brainly.com/question/26842818
#SPJ1
What is the kinetic energy,in J,of an Ar atom moving at a speed of 650 m/s
Answers
Answer:
1.40 × 10⁻²⁰ J
Explanation:
Step 1: Calculate the mass of 1 atom of argon
The molar mass of argon is 39.95 g/mol, that is, 6.02 × 10²³ atoms of Ar have a mass of 39.95 g. We can use this relation to find the mass of 1 atom of Ar.
\(\frac{39.95g}{1mol} \times \frac{1mol}{6.02 \times 10^{23}atom } =6.64 \times 10^{-23}g/atom\)
Step 2: Convert the mass of 1 atom of argon to kilograms
We will use the relationship 1 kg = 1,000 g.
\(6.64 \times 10^{-23}g \times \frac{1kg}{1,000g} =6.64 \times 10^{-26}kg\)
Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy of 1 atom of Ar moving at 650 m/s
\(E=\frac{1}{2} \times m \times v^{2} = \frac{1}{2} \times 6.64 \times 10^{-26}kg \times (650m/s)^{2} = 1.40 \times 10^{-20}J\)
The kinetic energy of an Ar atom at a speed of 650 m/s is 1.40 × 10⁻²⁰ J
Kinetic Energy:
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and to the square of its velocity:
K.E = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x \(m\) x \(v^{2}\)
Step 1: Calculate the mass of 1 atom of argon
The molar mass of argon is 39.95 g/mol, that is, 6.02 × \(10^{-23}\) atoms of Ar have a mass of 39.95 g. We can use this relation to find the mass of 1 atom of Ar.
\(\frac{39.95 g}{1 mol} * \frac{1 mol}{1,000 g} = 6.64 * 10^{-26} g/ atom\)
Step 2: Convert the mass of 1 atom of argon to kilograms
We will use the relationship 1 kg = 1,000 g.
6.64 x \(10^{-23}\) g x \(\frac{1 kg}{1,000g}\) = 6.64 x \(10^{-26}\) kg
Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy of 1 atom of Ar moving at 650 m/s
E= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x \(m\) x \(v^{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 6.64 x \(10^{-26}\) kg x (650 m/s)² = 1.40 x \(10^{-20}\) J
Learn more:
https://brainly.com/question/12337396
How do I balance these equations? Please explain so I can learn how.

Answers
One mole of CS₂ and two moles of H₂S are formed as products and 3 moles of CH₄ are leftover.
What is the limiting reagent?A limiting reagent is a reactant that is fully exhausted from the reaction mixture at the completion of a reaction. The limiting reactant will decide the maximum amount of product.
Given, a balanced chemical equation of the reaction between methane and sulphur is:
\(CH_4 + 4S\longrightarrow CS_2 +2H_2S\)
Given, the number of moles of the sulphur = 4
The number of moles of methane = 4
From the chemical reaction, one mole of methane reacts with four moles of sulphur. Therefore, four moles of sulphur fully react with one mole of methane and three moles of methane leftover.
Learn more about limiting reagents, here:
brainly.com/question/26905271
#SPJ1
The bulb lights up in the circuit. Only two rods are conductors of electricity. Which one of the rods, X, Y or Z is definitely a conductor of electricity? Explain why.
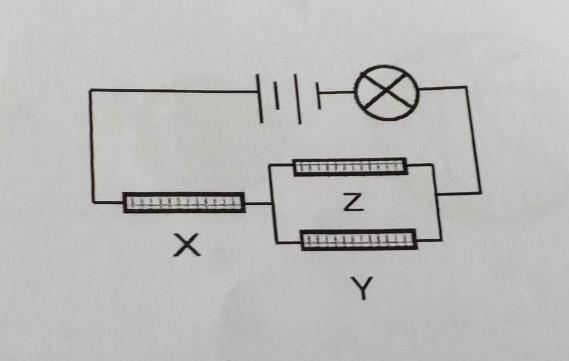
Answers
Answer: Rod X.
Explanation:
Ok, the electricity starts in the top left part. First, it must travel in the X rod, then it keeps traveling until it reaches the parallel path, and it can go to the Z rod, to the Y rod, or to both of them, and then it reaches the bulb (the circle with a X inside of it).
We know that two rods are conductors of electricity.
Now, suppose the case where rods Z and Y are the ones that conduct electricity, this means that X does not conduct electricity, then when the current reaches to X it stops (because X does not conduct) then the electricity never reaches the rods Z and Y, and then the electricity never reaches the bulb, but we know that the bulb lights up, so we must have that X is one of the conducting rods.
Then, if for example, Y does not conduct electricity, the electricity still can run through the Z rod and eventually reach the bulb.
So we can conclude that the rod that is definitely a conductor of electricity is rod X
Which is composed of alkenes?
welding torch fuel
polystyrene cups
gasoline
synthesized dyes
Answers
Answer:
a. welding torch fuel
Answer:
welding torch fuel
Explanation:
What mass of CaCl2 (in g ) should the chemist use?
Answers
The mass of the solute required is 250.25 g.
What is the mass of the solute?We know that the number of moles of the solute can be used to obtain the mass of the solute that is required. We can now try to find the mass of the solute that is required.
Concentration of the solution = 0.350M
Volume of the solution = 6.5 L
Number of moles of the solute = 0.350M * 6.5 L
= 2.275 moles
We now have the mass of the solute as;
2.275 moles * 110 g/mol
= 250.25 g
Th measured mass of the solute that we would have to use is 250.25 g.
Learn more about solute:https://brainly.com/question/7932885
#SPJ1
Missing parts;
A chemist wants to make 6.5 L of a .350M CaCl2 solution. What mass of CaCl2(in g) should the chemist use?